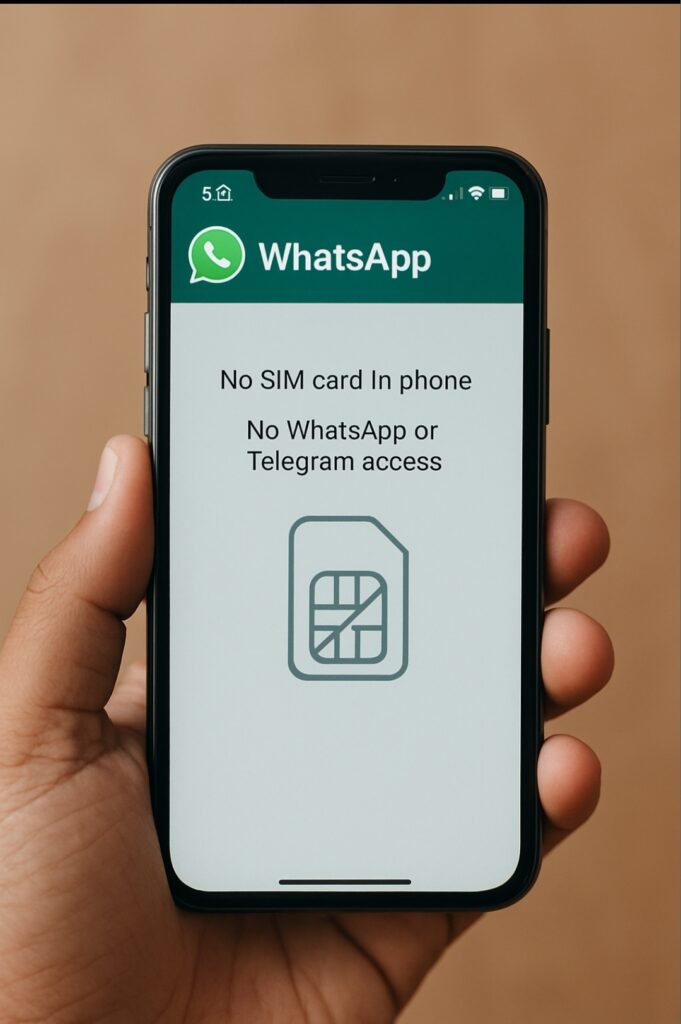
Navigating User Experience Challenges in Messaging Apps Amid India’s New SIM Card Mandate
The way millions of Indians communicate digitally is on the cusp of a significant shift. Imagine a scenario where your favorite messaging app like WhatsApp or Telegram suddenly stops working because you removed your SIM card or switched to another. This seemingly simple change could disrupt everyday workflows, customer interactions, and even employee communications. For CX and EX leaders, these changes mean rethinking engagement strategies, ensuring uninterrupted service, and balancing security with convenience.
India’s recent directive mandates that popular messaging platforms enforce continuous SIM card presence for app access, aiming to close cybersecurity loopholes. This presents new challenges for user experience (UX) design, customer trust, and operational continuity. The move also signals unprecedented telecom-style regulation for app-based communications—reshaping the digital communication landscape.
Understanding India’s Telecom Cybersecurity Amendment Rules, 2025
The Department of Telecommunications (DoT) released the Telecommunication Cybersecurity Amendment Rules, 2025, requiring apps like WhatsApp, Telegram, Signal, Snapchat, and others to bind accounts permanently to the SIM card used during account registration. Users must have the specific active SIM in their devices at all times to access these apps. Any SIM removal or inactivity disables app functionality.
Additional rules include periodic logouts from web versions every six hours, necessitating QR code authentication on the mobile device to ensure genuine user-device interaction. The government’s goal is to enhance traceability between users, their mobile numbers, and devices to curb fraud and unauthorized account access.
CX Implications: Balancing Security and Seamless Engagement
For customer experience professionals, this seamlessness-security tradeoff is critical. Messaging apps are crucial touchpoints for customer support, marketing, and real-time communication. Any disruption due to SIM binding could:
- Lead to frustration from forced app logouts or service interruptions.
- Affect multi-device users who rely on WhatsApp Web or desktop apps.
- Challenge remote and hybrid workforce communication if SIM cards are not consistently used.
On the other hand, tighter security protocols promise fewer spam and fraud interactions, which directly impact customer trust and reduce negative experiences. Organizations must now prepare for collateral impacts across customer journeys and internal communications.
Cybersecurity Context: Addressing Fraud While Facing Expert Debate
Current apps authenticate users mostly during setup, then operate independently of the SIM card. This gap enables fraudsters to misuse app accounts after SIM switches or deactivation. India recorded a monthly loss of approximately 1,000 crore rupees (about $120 million) to cyber fraud in early 2025, with a significant portion attributed to overseas-origin scams exploiting these weaknesses.
The Cellular Operators Association of India (COAI) advocated for persistent SIM binding to strengthen verification and accountability. The move aligns with security best practices already mandated in banking and digital payment apps, where SIM and biometric binding reduce unauthorized access.
However, cybersecurity experts are divided. Some argue SIM binding only offers incremental benefits since criminals can obtain new SIM cards via forged documents. Others emphasize that mobile numbers remain India’s strongest form of digital identity, and mandatory SIM-device linkage can tighten security frameworks.
Case Study Parallels: Financial Sector Security Mandates
India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI) and banking platforms already enforce strict SIM controls. Frequent verification and device binding reduce fraud significantly in financial transactions, an insight applicable to messaging platforms. SEBI’s proposals to link SIM cards to trading accounts with biometrics underscore an emerging national cybersecurity trend focused on persistent identity assurance.
Migrating similar practices to communication apps could fortify safeguards against fraud but must be paired with robust user education and contingency planning to avoid service disruptions during SIM changes or device upgrades.
Practical Recommendations for CX/EX Leaders
To effectively adapt, CX and employee experience (EX) leaders should:
- Communicate proactively: Inform customers about upcoming changes and how they might affect app usage.
- Design for resilience: Develop multi-channel support plans to ensure uninterrupted service when SIM binding causes temporary downtime.
- Train employees: Equip frontline staff with knowledge to assist users facing app access issues.
- Monitor feedback: Collect real-time data to quickly identify and resolve SIM binding-related experience issues.
- Balance security with convenience: Advocate for app vendors and regulators to implement user-friendly SIM verification methods.
Conclusion
India’s mandatory SIM card binding rule is a groundbreaking policy intersecting cybersecurity and digital user experience. It reflects growing governmental intent to tighten control over digital identifiers amidst rising cybercrime. For CX professionals, navigating this transition requires balancing security priorities with the need for frictionless communication.
This mandate challenges legacy concepts of app access but also opens avenues to rebuild trust with highly secure, accountable communication platforms. Forward-thinking CX and EX strategies will ensure that security gains do not come at the cost of customer frustration or employee inefficiency, making this a defining moment in India’s digital experience evolution.
By understanding the regulatory context, security rationale, and experience implications, CX leaders can proactively steer their organizations through these changes and harness them for stronger customer and employee engagement outcomes.