Generative AI in CX: Overcoming Obstacles to Unlock Potential
Generative AI is rapidly advancing in the customer experience (CX) sector, promising substantial benefits but also presenting significant challenges. As businesses seek to incorporate these technologies, a gap remains between what AI technology can offer and what companies are ready to adopt. The rise of generative AI in CX has been a game-changer, yet many businesses are struggling to fully embrace this evolution.
The Gap Between Technology and Adoption
As vendors roll out generative AI innovations at an unprecedented pace, adoption by businesses has not kept up. According to Zendesk’s CX Trends 2025 report, a significant number of businesses remain hesitant to deploy AI due to budget constraints, a lack of expertise, and insufficient internal support. Additionally, a survey of 2,300 senior IT decision-makers found that over half had not yet aligned their generative AI strategies with business needs. While 39% have made substantial investments in generative AI, many others are still in the pilot or trial stages.
Nevertheless, the technology is progressing. Companies like Salesforce and HubSpot are leading the way, incorporating generative AI into their platforms while also investing in AI startups to strengthen their future capabilities. The growing prevalence of AI-powered customer service tools, such as generative AI bots, is reshaping how businesses approach CX.
The Promise of Generative AI in Customer Service
Generative AI has found a home in customer service and contact centers, with AI-powered bots becoming integral to many CX operations. These bots, when paired with reasoning engines, can make simple decisions autonomously and handle tasks that were once more labor-intensive. They offer businesses the potential for greater efficiency, primarily by retrieving and summarizing information more effectively than their predecessors.
However, implementing generative AI is far from simple. Businesses need to invest significant effort into organizing their data and aligning their processes with the capabilities of AI. According to John Seeds, chief marketing officer at TTEC Digital, businesses should first clean up their internal data, eliminating inconsistencies and duplication, before deploying generative AI for customer-facing tasks. By doing so, companies can enhance self-service, reduce inbound queries, and streamline their contact center operations.
The Role of Data in Generative AI Adoption
A successful generative AI implementation hinges on well-organized data. For marketing and e-commerce teams, AI tools like those from Google, Salesforce, and Sitecore have enabled content generation. These AI solutions can help create initial drafts for marketing campaigns or websites, providing a foundation upon which creatives can build.
However, AI tools cannot perform at their best without access to accurate, structured data. Companies must invest in ensuring their data is clean and well-organized to enable generative AI to function effectively in marketing and customer service contexts.
The Impact of ChatGPT on CX
The introduction of ChatGPT in late 2022 revolutionized generative AI in CX. For John Ball, senior vice president at ServiceNow, the technology’s rapid development has unlocked possibilities that were once only theoretical. Tasks such as chat and email response recommendations no longer require extensive manual work, thanks to the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT.
Similarly, Clara Shih, who previously led AI at Salesforce, recalled her initial skepticism about generative AI but was quickly won over by its capabilities. The sudden surge in adoption of generative AI across industries, from small startups to major corporations, highlighted the immense potential of the technology.
The Future of AI Autonomy in CX
Despite the benefits of generative AI, many questions remain, especially concerning the autonomy of AI agents. Can AI bots make decisions that benefit customers without overstepping boundaries? What if a bot makes a poor decision, either in favor of the company or the customer? Ensuring that generative AI operates within predefined parameters, while still being able to provide valuable assistance, remains an open challenge.
One example of this is Trimedx, a company managing clinical hardware for hospitals. Their CIO, Brad Jobe, believes generative AI can save time in documentation processes but recognizes that it will take time before AI can handle complex decisions autonomously. The company plans to deploy generative AI to fill out reports for its 2.5 million devices in the field, providing an attractive return on investment.
Regulatory and Copyright Challenges
As generative AI continues to gain ground in CX, businesses must also contend with a shifting regulatory landscape. The U.S. government has already begun addressing consumer protection issues related to CX, such as the recent ban on “junk fees” in the hospitality industry. New regulations could impact how generative AI is used in customer service, requiring businesses to ensure compliance in their processes.
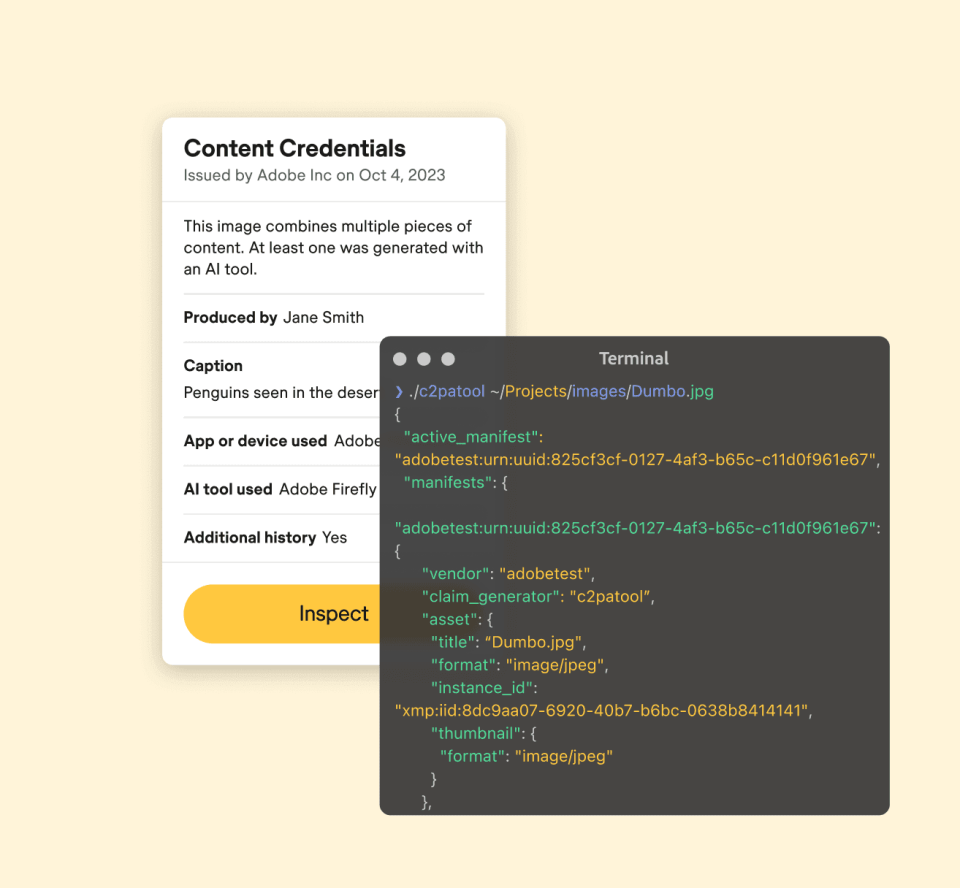
Additionally, there are growing concerns about copyright infringement as businesses incorporate generative AI into their workflows. Adobe’s Content Authenticity Initiative (CAI) aims to combat this by creating transparency in how digital content is generated and edited. By embedding metadata that tracks the history of an image’s creation and edits, CAI seeks to ensure that businesses can demonstrate the authenticity of their content.
Navigating the Future of Generative AI in CX
Generative AI offers immense potential for enhancing CX, but businesses face a variety of obstacles in fully realizing its benefits. Data management, compliance, and the limitations of current AI autonomy are just a few of the challenges that must be addressed. Despite these hurdles, the technology is advancing rapidly, and its potential to improve customer service, reduce costs, and enhance the efficiency of CX operations is undeniable.
As companies continue to integrate generative AI into their processes, they must stay vigilant in managing their data, understanding regulatory requirements, and developing AI systems that maintain high standards of customer satisfaction. The future of generative AI in CX looks promising, but success will depend on how effectively businesses can navigate these challenges and leverage AI’s capabilities to their fullest extent.
With these ongoing developments, one thing is clear: Generative AI is poised to transform CX in ways we are just beginning to understand. The journey towards full adoption may be complex, but the rewards for those who successfully integrate this technology will be substantial.