Why CX Leaders Can’t Ignore Java in 2026
How AI-Driven Experiences, Cloud Economics, and Platform Choices Are Reshaping Customer Journeys
Ever watched a flawless AI demo collapse in production—slow responses, ballooning cloud bills, and frontline teams blaming “the system”?
That breakdown rarely starts in the CX layer. It starts deeper. In runtime choices, licensing decisions, and invisible platform debt.
In 2026, Java sits at the center of that tension.
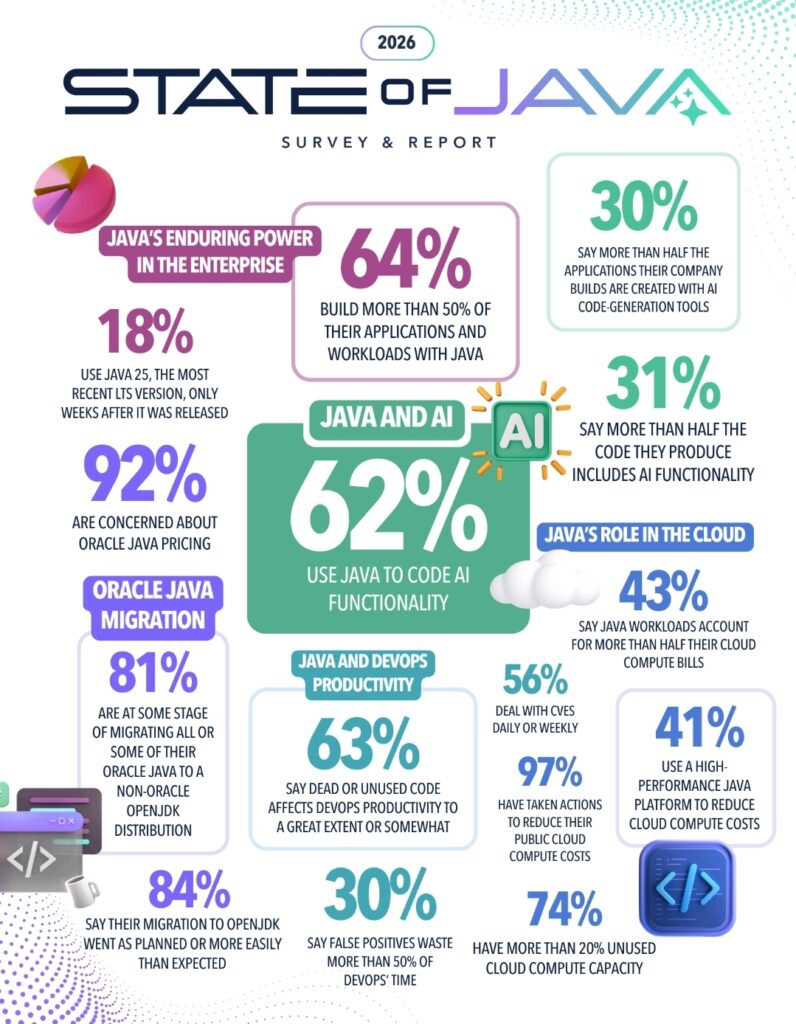
According to Azul’s 2026 State of Java Survey, 62% of enterprises now use Java to power AI functionality, while 92% worry about Oracle Java pricing. At the same time, 41% rely on high-performance Java platforms to reduce cloud compute costs.
For CX and EX leaders, this is not a developer story.
It is a journey reliability, cost predictability, and experience scalability story.
Let’s unpack why.
Java in 2026: What Is Driving Java’s CX Relevance in 2026?
Java has quietly become the runtime behind AI-powered, always-on customer experiences.
As AI moves from pilots to production, enterprises embed models into existing systems. Most of those systems already run on Java. Instead of rebuilding journeys from scratch, teams extend what exists.
That shift changes Java’s role—from backend utility to experience infrastructure.
Java in 2026: Why this matters to CX leaders
- AI experiences fail when runtimes stall.
- Customers feel latency before teams see dashboards.
- Cost overruns kill innovation budgets.
Java sits in the blast radius of all three.
Why Are CX Teams Feeling Platform Pain More Acutely Now?
Because AI amplifies every inefficiency already hiding in enterprise systems.
The Azul survey highlights a pattern CX leaders recognize instantly:
- 74% of organizations report over 20% unused cloud compute capacity
- 63% say dead or unused code hurts productivity
- 56% face Java-related CVEs weekly or daily
AI workloads intensify usage spikes, startup times, and security noise.
When runtimes behave unpredictably, teams overprovision “just in case.”
That safety margin becomes experience tax.
How Does Java Power AI-Driven Customer Journeys Today?
Java runs the orchestration layer that turns models into usable experiences.
While Python dominates experimentation, Java dominates production:
- API gateways
- Transaction processing
- Event streaming
- Personalization engines
- Fraud detection
- Conversational backends
The survey shows 31% of enterprises now embed AI in more than half of their Java applications.
This hybrid reality defines modern CX stacks:
- Models infer.
- Java systems decide, scale, and respond.
What Capabilities Do CX-Critical Java Platforms Need Now?
Stability alone is no longer enough. Performance intelligence matters.
Survey respondents ranked these as top requirements:
- Long-term support for modern Java versions (35%)
- Built-in security features (34%)
- Observability insights (32%)
- Large data access support (30%)
- LLM integration (30%)
For CX leaders, this translates to:
- Faster cold starts for digital journeys
- Fewer surprise outages during traffic surges
- Clear visibility into runtime behavior
- Lower mean time to resolution
Why Are Enterprises Migrating Away from Oracle Java?
Pricing unpredictability breaks CX planning cycles.
Since Oracle’s employee-based pricing model launch, concern has exploded:
- 92% express pricing concern
- 81% are migrating or planning migration
- 63% intend to migrate their entire Java estate
- 21% have already faced audits
From a CX lens, this matters because:
- Budget volatility delays roadmap commitments
- Audit fear freezes modernization
- Licensing debates stall AI rollouts
Experience leaders need platforms that do not hijack strategy discussions.
How Does OpenJDK Migration Affect CX and EX Outcomes?
It restores control over pace, cost, and experimentation.
OpenJDK-based platforms offer:
- Licensing predictability
- Vendor choice
- Compatibility with existing applications
That freedom enables:
- Faster AI integration
- Safer refactoring of legacy journeys
- Confidence to remove dead code
- Reduced compliance anxiety
CXQuest research consistently shows that organizational confidence accelerates experience improvement.
How Are High-Performance Java Platforms Reducing Cloud Costs?
By turning efficiency into a CX investment pool.
The survey reveals:
- 97% of enterprises actively reduce cloud spend
- 41% use high-performance Java platforms to do so
- Among Java-heavy organizations, adoption jumps to 81%
Performance gains mean:
- Fewer instances
- Faster response times
- Less overprovisioning
Every saved compute dollar can fund:
- Journey redesign
- Agent enablement
- Personalization experiments
Why Dead Code and CVE Noise Hurt CX More Than Leaders Realize
Because invisible technical debt creates visible experience friction.
Dead code slows:
- Release cycles
- Incident response
- Security triage
False-positive CVEs waste time:
- 30% of teams lose over half their time chasing noise
From the CX chair, this manifests as:
- Delayed feature launches
- Inconsistent journey fixes
- Burned-out DevOps teams
- Risk-averse behavior
Experience debt compounds quietly.
A CX-Oriented Framework: The Java Experience Stack
Think in layers, not languages.
1. Experience Layer
Channels, journeys, interactions.
2. Intelligence Layer
AI models, decision engines, personalization logic.
3. Orchestration Layer (Java’s Core Role)
APIs, transactions, workflow coordination.
4. Runtime Layer
Performance, startup behavior, memory use.
5. Economics Layer
Licensing, cloud efficiency, audit risk.
Break any layer—and the customer feels it.
Common Pitfalls CX Leaders Still Make
These mistakes keep repeating across enterprises.
- Treating Java as “engineering-only” territory
- Ignoring runtime choices until outages occur
- Funding AI pilots without production readiness
- Accepting cloud waste as unavoidable
- Letting licensing fear stall modernization
Each pitfall weakens trust—internally and externally.
What This Means for CX Strategy in 2026
Experience leadership now requires platform literacy.
Not deep coding knowledge.
But enough fluency to ask better questions:
- Are our AI journeys production-ready?
- Where does runtime friction show up?
- What costs are we hiding in inefficiency?
- Which decisions slow teams silently?
CX excellence increasingly depends on invisible infrastructure choices.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Java impact customer experience directly?
Java affects response times, system stability, and scalability. Customers feel delays instantly.
Is Java still relevant with AI-first architectures?
Yes. Java runs the production systems that operationalize AI at scale.
Why should CX leaders care about Java licensing?
Unpredictable licensing disrupts budgets, roadmaps, and modernization timelines.
How does cloud cost optimization improve CX?
Lower costs free budgets for innovation, personalization, and frontline tools.
What role does observability play in CX outcomes?
Better runtime visibility reduces outages and speeds issue resolution.
Actionable Takeaways for CX Leaders
Use this as a practical checklist.
- Map critical customer journeys to underlying runtime platforms.
- Audit AI features for production scalability, not demo performance.
- Partner with engineering on Java platform strategy discussions.
- Quantify cloud waste tied to runtime inefficiency.
- Prioritize observability that links system behavior to CX metrics.
- Reduce dead code as an experience reliability initiative.
- Treat licensing predictability as a CX enabler, not a legal detail.
- Reinvest performance savings into journey innovation.
Final Thought
In 2026, great CX is built as much on runtimes as on roadmaps.
Java’s evolution—toward AI enablement, cost efficiency, and operational clarity—offers CX leaders a quiet advantage.
Those who see it early will ship faster, scale smarter, and disappoint customers far less often.
That’s not a developer story.
That’s an experience strategy.