Revolutionizing Healthcare: How AI-Powered Childhood Malnutrition Detection Is Transforming Patient Experience
The convergence of artificial intelligence and healthcare has reached a pivotal moment. Consequently, researchers at IIT-AIIMS Jodhpur have developed DomainAdapt, a groundbreaking AI framework that transforms childhood malnutrition detection through simple photographs. Moreover, this innovation addresses critical gaps in traditional healthcare delivery while dramatically improving the customer experience for families seeking timely, accurate nutritional assessments for their children.
The Current Challenge in Malnutrition Detection
Healthcare systems worldwide struggle with childhood malnutrition, which affects over 150 million children under five years old globally. Furthermore, traditional anthropometric measurement methods present significant barriers to efficient care delivery. These conventional approaches require extensive physical measurements including height, weight, and mid-upper arm circumference (MUAC), which healthcare workers must collect manually.
Additionally, traditional methods suffer from inherent limitations that directly impact patient experience. Healthcare professionals face challenges with subjective assessments, time-consuming procedures, and scalability issues in resource-limited settings. Consequently, these barriers create frustrating delays for families and often result in missed opportunities for early intervention.
Understanding DomainAdapt: The Technology Behind the Breakthrough
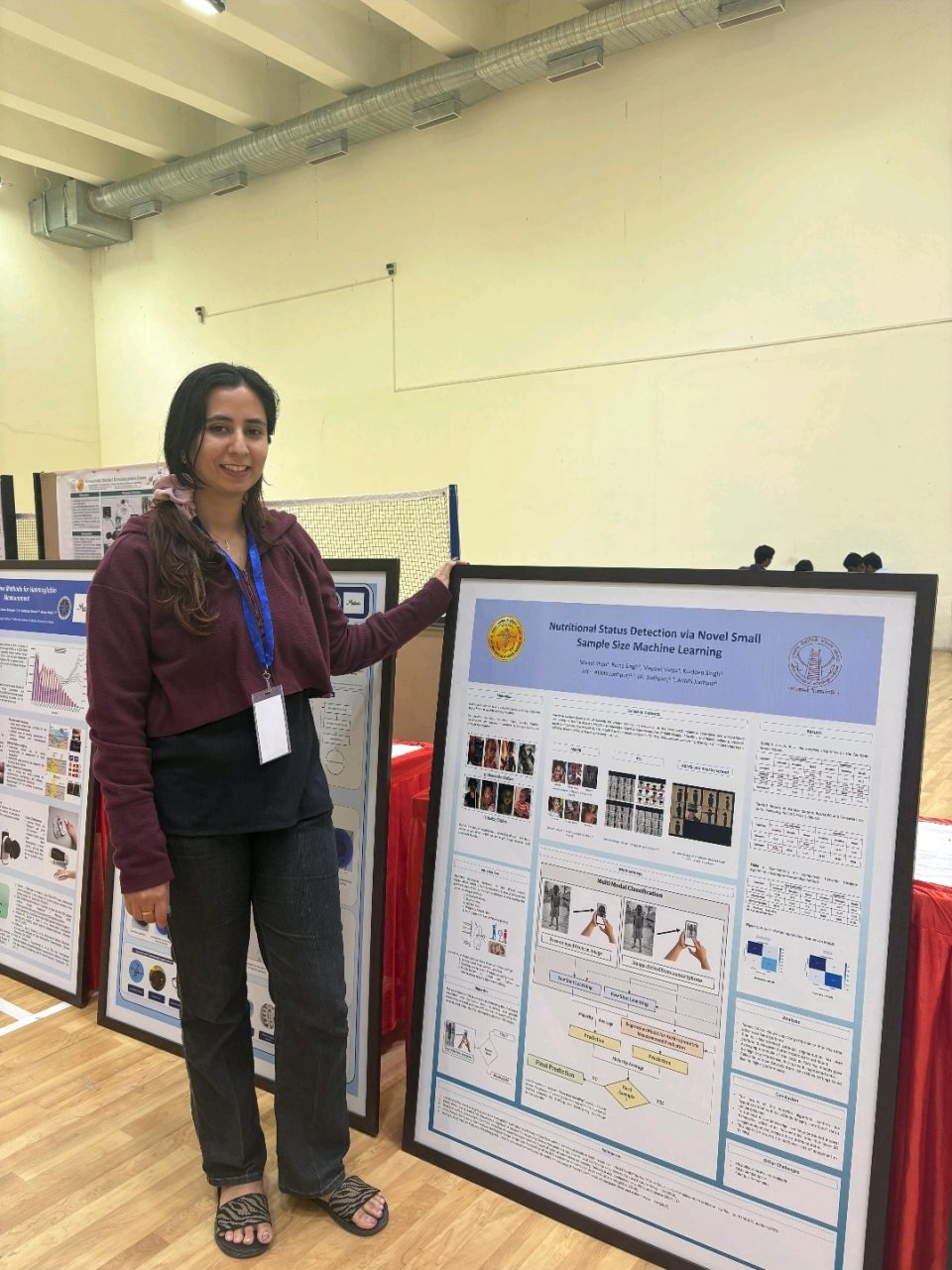
The DomainAdapt framework represents a significant advancement in multitask learning for healthcare applications. Specifically, this novel system dynamically adjusts task weights using domain knowledge and mutual information, allowing simultaneous prediction of key anthropometric measures. Furthermore, it classifies malnutrition-related conditions including stunting, wasting, and underweight status from simple photographs.
The technology utilizes computer vision algorithms to analyze multiple data points from images. Additionally, the system processes multipose photographs to extract meaningful nutritional indicators without requiring traditional physical measurements. Subsequently, this approach eliminates the need for complex and time-consuming anthropometric assessments that often create barriers to care access.
The AnthroVision Dataset: Powering Accurate Assessments
Supporting the DomainAdapt framework is the AnthroVision dataset, comprising 16,938 multi-pose images from 2,141 children. Moreover, this comprehensive dataset was collected across both clinical settings at AIIMS Jodhpur and community locations including government schools in Rajasthan. Furthermore, the dataset captures diverse backgrounds, clothing, and lighting conditions, ensuring robust performance across various real-world scenarios.
The dataset’s diversity enhances the system’s reliability in different healthcare environments. Consequently, healthcare providers can confidently use the technology regardless of their specific setting or patient demographics. Therefore, this comprehensive approach ensures equitable access to advanced malnutrition screening tools.
Customer Experience Transformation in Healthcare
The implementation of AI-powered malnutrition detection fundamentally transforms the healthcare customer experience. Previously, families faced lengthy assessment processes requiring multiple visits and extensive measurements. However, the new system enables rapid, accessible screening through simple photograph capture.
Streamlined Assessment Process
Healthcare providers can now complete malnutrition assessments in minutes rather than hours. Additionally, the photograph-based approach reduces stress for children who might otherwise resist traditional measurement procedures. Furthermore, parents appreciate the non-invasive nature of the assessment, which eliminates anxiety often associated with medical examinations.
Enhanced Accessibility
The technology particularly benefits families in resource-limited settings where traditional screening equipment may be unavailable. Moreover, the scalable nature of the AI system enables deployment in remote areas previously underserved by comprehensive nutritional assessment programs. Consequently, more children gain access to timely malnutrition screening and intervention.
Clinical Performance and Validation
Rigorous testing demonstrates that DomainAdapt significantly outperforms existing multitask learning methods. Furthermore, the system accurately predicts anthropometric measures including height, weight, MUAC, and head circumference from photographs alone. Additionally, validation studies confirm the framework’s reliability across diverse populations and settings.
The system’s performance metrics indicate high accuracy in identifying various forms of malnutrition. Specifically, the technology demonstrates strong sensitivity and specificity for detecting stunting, wasting, and underweight conditions. Therefore, healthcare providers can trust the system’s recommendations for further clinical intervention when necessary.
Economic Impact and Healthcare Costs
Malnutrition imposes substantial economic burdens on healthcare systems globally. Research indicates that untreated malnutrition costs approximately $3.0 billion annually in direct medical expenses in countries like the Netherlands alone. Furthermore, when including indirect costs from lost productivity, total malnutrition-related expenses reach $5.4 billion per year.
The AI-powered screening system offers significant cost reduction potential. Moreover, early detection through accessible screening prevents complications that lead to expensive emergency interventions. Additionally, the technology’s scalability enables widespread deployment without proportional increases in healthcare personnel costs.
Addressing Traditional Method Limitations
Conventional anthropometric measurements face numerous practical challenges that impact care quality. Healthcare workers often struggle with measurement accuracy, particularly when assessing children with mobility difficulties or in community settings. Furthermore, traditional methods require specialized equipment and trained personnel, limiting accessibility in resource-constrained environments.
Mid-upper arm circumference (MUAC) measurement, while valuable for malnutrition screening, presents specific challenges. Healthcare providers must ensure proper positioning and measurement technique to obtain accurate results. However, the AI-powered approach eliminates these technical barriers while maintaining diagnostic accuracy.
Digital Transformation in Healthcare Context
The DomainAdapt framework exemplifies broader digital transformation trends in healthcare delivery. Specifically, AI-powered screening tools represent a shift toward more efficient, accessible, and patient-centered care models. Furthermore, these technologies enable healthcare systems to optimize resource allocation while improving clinical outcomes.
Digital health innovations increasingly focus on reducing administrative burdens while enhancing patient experience. Moreover, AI-driven solutions like malnutrition screening systems free healthcare workers to focus on direct patient care rather than time-consuming manual assessments. Consequently, both providers and patients benefit from more efficient care delivery processes.
Multitask Learning Applications in Healthcare
The success of DomainAdapt highlights the broader potential of multitask learning in medical applications. These sophisticated AI systems can simultaneously address multiple healthcare challenges using shared computational resources. Furthermore, multitask approaches often demonstrate superior performance compared to single-task alternatives by leveraging complementary information across related problems.
Healthcare applications of multitask learning extend beyond malnutrition detection. Additionally, these systems show promise for disease diagnosis, prognosis prediction, and treatment optimization across various medical specialties. Therefore, the DomainAdapt framework represents just one example of how multitask learning can revolutionize healthcare delivery.
Global Health Implications
The AI-powered malnutrition detection system addresses critical global health challenges. With childhood malnutrition affecting millions worldwide, accessible screening tools become essential for achieving public health goals. Moreover, the technology’s potential for deployment in low-resource settings could significantly impact malnutrition reduction efforts in developing regions.
International health organizations emphasize the importance of early malnutrition detection for preventing long-term health consequences. Furthermore, AI-powered screening systems enable rapid identification of at-risk children, facilitating timely interventions that can prevent irreversible developmental damage. Consequently, widespread adoption of such technologies could contribute substantially to global malnutrition reduction targets.
Future Directions and Research Opportunities
The development of DomainAdapt opens numerous avenues for future research and application. Researchers continue exploring ways to enhance the system’s accuracy and expand its capabilities. Additionally, ongoing work focuses on integrating the technology with existing healthcare information systems to streamline clinical workflows.
Future developments may include real-time screening capabilities through mobile applications, enabling parents and community health workers to conduct preliminary assessments. Moreover, researchers are investigating applications of similar AI approaches to other nutritional assessment challenges beyond childhood malnutrition.

Implementation Challenges and Solutions
While the technology offers significant benefits, implementation requires careful consideration of practical challenges. Healthcare systems must ensure adequate training for personnel using AI-powered screening tools. Furthermore, integration with existing clinical workflows requires thoughtful planning to maximize adoption and effectiveness.
Data privacy and security considerations remain paramount when implementing AI systems in healthcare settings. Additionally, healthcare organizations must establish protocols for validating AI recommendations and maintaining appropriate clinical oversight. Therefore, successful implementation requires comprehensive change management strategies that address both technical and organizational factors.
The revolutionary AI-powered malnutrition detection system developed by IIT-AIIMS Jodhpur represents a significant advancement in healthcare customer experience. By transforming complex, time-consuming assessments into simple, accessible screenings, the technology addresses critical barriers to malnutrition detection while improving care accessibility. Furthermore, the system’s potential for widespread deployment could substantially impact global health outcomes, particularly in resource-limited settings where traditional screening methods face the greatest challenges.
As healthcare continues evolving toward more patient-centered, technology-enabled delivery models, innovations like DomainAdapt demonstrate the transformative potential of AI in creating more effective, accessible, and equitable healthcare systems for vulnerable populations worldwide.