The convergence of artificial intelligence and customer experience represents one of the most transformative shifts in modern business, yet it brings unprecedented ethical challenges that organizations must navigate carefully. As 73% of consumers expect more AI interactions in their daily lives, the imperative for ethical implementation has never been more critical. This comprehensive analysis explores the landscape of AI ethics projects in customer experience, examining frameworks, real-world implementations, and strategic approaches that enable organizations to harness AI’s power while upholding fundamental ethical principles.
Understanding the AI Ethics Imperative in Customer Experience
Ethical AI in customer experience encompasses the responsible development, deployment, and management of AI systems that prioritize fairness, transparency, and respect for customers’ privacy and values. The stakes are particularly high in customer-facing applications where AI decisions directly impact individual experiences and can perpetuate or amplify existing biases. As Dr. Timnit Gebru, a prominent AI ethics researcher, noted: “Machines don’t have feelings—but they can still inherit our flaws”.
The business case for ethical AI extends far beyond compliance. According to recent Accenture research, the top 12% of companies by growth are 53% more likely to build AI responsibly by design, reaping benefits in customer experience and ESG performance. Organizations that proactively implement ethical AI practices position themselves to build customer trust, safeguard brand reputation, and unlock sustainable competitive advantages in an increasingly AI-driven marketplace.

Core Categories of AI Ethics Projects in Customer Experience
Bias Detection and Fairness Auditing
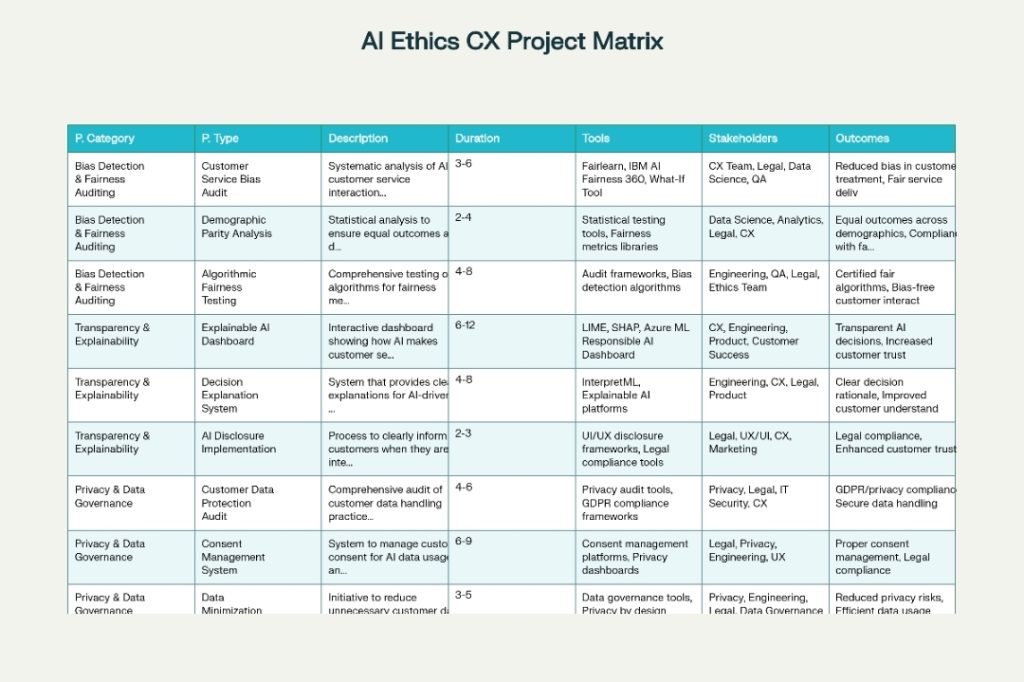
Bias detection and fairness auditing represent perhaps the most critical category of AI ethics projects in customer experience. These initiatives focus on identifying and mitigating discriminatory patterns in AI systems that could lead to unfair treatment of certain51% of micro-firms face discrimination compared to non-micro firms in AI-driven decision-making systems, highlighting the pervasive nature of algorithmic bias.
Customer Service Bias Audits involve systematic analysis of AI customer service interactions to identify disparities in treatment across demographics. These projects typically utilize tools like Fairlearn, IBM AI Fairness 360, and What-If Tool to assess whether AI chatbots, routing systems, or decision-support tools exhibit bias based on factors such as accent, language, gender, or geographic location. For instance, bias can emerge when AI systems are trained on non-inclusive datasets, resulting in poor performance for users who speak different languages or dialects.
Demographic Parity Analysis projects focus on ensuring equal outcomes across different customer groups through statistical testing and fairness metrics evaluation. These initiatives implement mathematical frameworks to measure and correct disparities in AI-driven outcomes, ensuring that customer service quality remains consistent regardless of demographic characteristics.
Algorithmic Fairness Testing represents a more comprehensive approach, involving end-to-end testing of AI algorithms using established fairness frameworks. Organizations like Pegasystems have developed tools like the Ethical Bias Check, which flags potentially discriminatory offers and messages before they reach customers, allowing companies to adjust algorithms to provide fairer outcomes.
Transparency and Explainability Initiatives
Transparency and explainability projects address the “black box” problem inherent in many AI systems, ensuring customers understand when and how AI influences their experience. The EU AI Act mandates that every AI-supported dialogue must be clearly labeled as such, making transparency initiatives not just ethical imperatives but legal requirements.
Explainable AI Dashboard projects create interactive interfaces that show how AI makes customer service decisions. These systems utilize techniques like LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations), SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations), and Azure ML Responsible AI Dashboard to provide clear explanations of AI reasoning. Companies implementing these systems report improved customer trust and satisfaction as users better understand AI-driven interactions.
Decision Explanation Systems go beyond dashboards to provide real-time explanations for AI-driven customer decisions. These systems are particularly valuable in high-stakes scenarios such as loan approvals, insurance claims, or account restrictions, where customers deserve to understand the rationale behind AI decisions that affect their lives.
AI Disclosure Implementation projects focus on the procedural aspects of transparency, ensuring customers are informed when they interact with AI systems. This includes developing clear notification mechanisms, user interface design, and escalation pathways to human agents when customers prefer human interaction.
Privacy and Data Governance Projects
Privacy and data governance initiatives address the fundamental challenge of protecting customer data while enabling AI innovation. With the EU’s GDPR and emerging privacy regulations worldwide, these projects have become essential for legal compliance and customer trust.
Customer Data Protection Audits involve comprehensive reviews of how customer data is collected, stored, processed, and used in AI systems. These audits ensure compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA while implementing privacy-by-design principles in AI development. Organizations conducting these audits often discover opportunities to reduce data collection and improve security practices without compromising AI performance.
Consent Management Systems enable customers to understand and control how their data is used in AI applications. These systems provide granular control over data usage, allowing customers to opt-in or opt-out of specific AI features while maintaining transparency about data processing practices.
Data Minimization Projects focus on reducing unnecessary customer data collection and retention in AI systems. These initiatives align with privacy regulations that require organizations to collect only data necessary for specific purposes and delete data when no longer needed.
Human Oversight and Control Frameworks
Human oversight and control projects ensure that AI systems augment rather than replace human judgment in customer interactions. The EU AI Act specifically requires human-in-the-loop systems, particularly in sectors where AI decisions can significantly impact human lives.
Human-in-the-Loop Systems establish frameworks where human agents can intervene in AI customer interactions when necessary. These systems include escalation triggers, override capabilities, and quality assurance mechanisms that ensure human oversight remains meaningful and effective. Companies implementing these systems report improved customer satisfaction and reduced liability risks.
AI Escalation Protocols define clear procedures for transitioning AI interactions to human agents based on complexity, customer preference, or system confidence levels. These protocols ensure seamless handoffs that maintain context and avoid customer frustration.
Agent Empowerment Tools provide customer service agents with AI-powered assistance while maintaining human control over final decisions. These tools include real-time coaching, knowledge recommendations, and decision support that enhance agent capabilities without replacing human judgment.
Compliance and Regulatory Alignment
Compliance and regulatory projects address the rapidly evolving legal landscape surrounding AI use in customer experience. The EU AI Act, effective from August 2024, represents the world’s first comprehensive AI regulation and sets the global standard for ethical AI deployment.
EU AI Act Compliance Programs involve comprehensive initiatives to ensure customer service AI systems meet regulatory requirements. These programs typically span 12-18 months and include risk classification, documentation requirements, transparency obligations, and ongoing monitoring systems. Organizations face potential fines of up to €35 million or 7% of global turnover for non-compliance.
Risk Assessment Frameworks establish systematic approaches to evaluate and manage AI risks in customer experience applications. These frameworks categorize AI systems based on their potential impact and implement appropriate controls and oversight mechanisms.
Ethics Committee Setup involves establishing governance structures to oversee ethical AI implementation across the organization. These committees typically include representatives from legal, technology, customer experience, and ethics teams to ensure comprehensive oversight of AI initiatives.
Implementation Timeline and Strategic Approach
Successfully implementing AI ethics projects requires a structured, phased approach that balances immediate compliance needs with long-term strategic objectives. Organizations should expect a 24-month timeline for comprehensive ethical AI transformation.
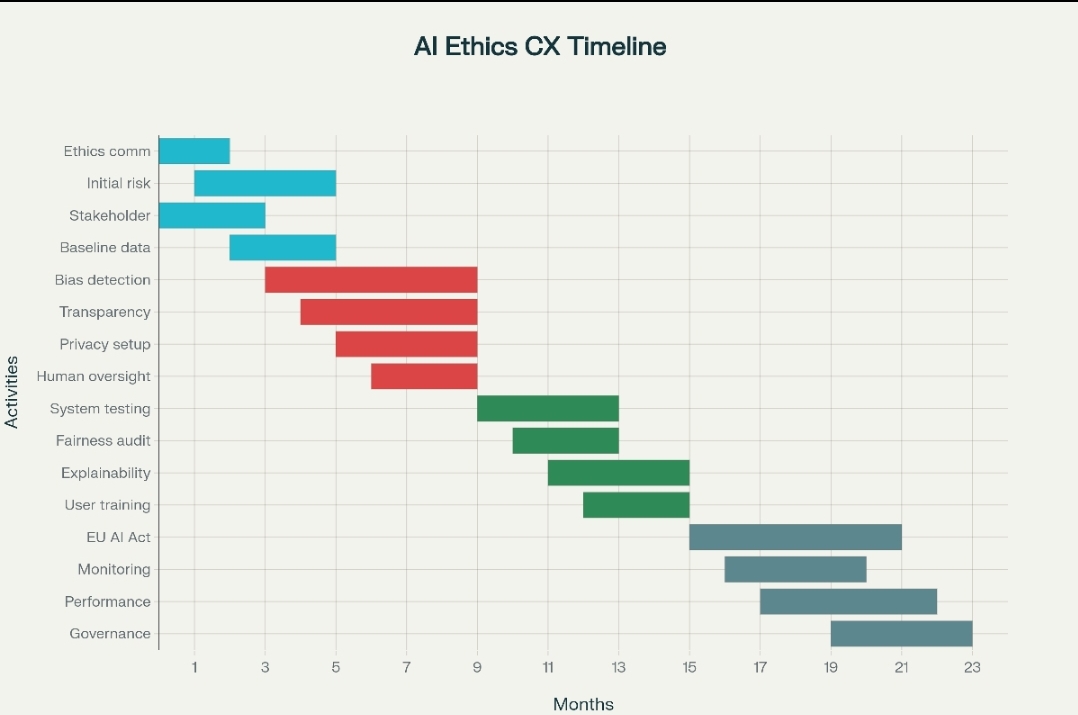
The Foundation and Assessment Phase (Months 1-6) focuses on establishing governance structures, conducting initial risk assessments, and aligning stakeholders around ethical AI principles. This phase includes setting up ethics committees, baseline data collection, and developing organizational AI ethics frameworks.
The Core Implementation Phase (Months 4-10) involves deploying key ethical AI systems including bias detection tools, transparency mechanisms, privacy frameworks, and human oversight protocols. This phase often represents the most resource-intensive period of the transformation.
The Integration and Testing Phase (Months 10-16) focuses on system integration, comprehensive testing, and validation of ethical AI implementations. This includes fairness auditing, explainability validation, and extensive user training programs to ensure effective adoption.
The Optimization and Compliance Phase (Months 16-24) involves finalizing regulatory compliance, establishing continuous monitoring systems, and implementing ongoing governance processes. This phase ensures sustainable ethical AI operations and prepares organizations for evolving regulatory requirements.
Real-World Case Studies and Success Stories
Several organizations have demonstrated the practical benefits of implementing ethical AI projects in customer experience. Trustap, a secure payments platform, implemented a comprehensive AI Ethics Charter that increased staff awareness of AI ethics and built a foundation for responsible data use. Their approach included review processes, data governance frameworks, and human-centered design principles that ensure AI technology aims to be beneficial while addressing potential concerns.
Europcar partnered with Devoteam to develop an ethically-driven AI chatbot for employee information retrieval. Their collaborative approach involved end-users and business operations throughout development, using agile methods for continuous ethical reviews to proactively identify and address potential biases. The project demonstrated that ethical AI implementation can improve both efficiency and service quality.
Microsoft’s AI for Earth initiative exemplifies how ethical AI principles can be applied at scale. The program demonstrates sustainability, transparency, and collaboration by providing detailed project information and partnering with diverse organizations to maximize positive impact. While not specifically customer service-focused, the initiative provides a model for how large organizations can implement ethical AI principles across their operations.
In the retail sector, companies have implemented AI bias testing initiatives that analyze customer service interactions for discriminatory patterns. These projects have revealed issues such as accent bias in AI systems, sentiment misclassification in emotion-detection tools, and script adherence bias that penalizes natural conversations. Organizations addressing these issues report improved customer satisfaction and reduced legal risk.
Tools and Technologies for Ethical AI Implementation
Organizations implementing AI ethics projects have access to a growing ecosystem of tools and platforms designed to support responsible AI development and deployment.
Bias Detection and Fairness Tools include Fairlearn, IBM AI Fairness 360, What-If Tool, and specialized bias detection algorithms. These tools enable organizations to assess algorithmic fairness, identify discriminatory patterns, and implement corrective measures before AI systems impact customers.
Explainability and Transparency Platforms such as LIME, SHAP, InterpretML, and Azure ML Responsible AI Dashboard provide capabilities for making AI decisions interpretable and transparent. These tools generate human-understandable explanations of AI predictions and enable organizations to communicate AI reasoning to customers and stakeholders.
Privacy and Data Governance Solutions include consent management platforms, privacy dashboards, and data governance frameworks that help organizations manage customer data responsibly while enabling AI innovation. These tools ensure compliance with privacy regulations while maintaining operational efficiency.
Comprehensive Responsible AI Platforms like Azure Machine Learning Responsible AI Dashboard integrate multiple ethical AI capabilities into unified interfaces. These platforms combine model performance assessment, fairness evaluation, interpretability analysis, error analysis, and counterfactual analysis to provide holistic views of AI system ethics and performance.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance Requirements
The regulatory environment for AI in customer experience is rapidly evolving, with the EU AI Act leading global efforts to establish comprehensive AI governance. The Act’s risk-based approach categorizes AI systems into four levels: unacceptable risk (prohibited), high risk (strict requirements), limited risk (transparency obligations), and minimal risk (self-regulation).
For customer service applications, AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants typically fall under limited-risk categories, requiring transparency obligations such as clear disclosure of AI interaction and human escalation options. However, AI systems used in credit scoring, employment screening, or other high-impact decisions may be classified as high-risk, requiring extensive documentation, human oversight, and regular auditing.
Key EU AI Act requirements for customer service include:
- Transparency obligations: Customers must know when they interact with AI systems
- AI-generated content labeling: Responses generated by AI must be clearly identified
- Restrictions on emotion recognition: Tools analyzing emotions from speech or facial expressions face strict limitations
Enforcement timelines are aggressive, with prohibited AI practices banned since February 2025, and full compliance required by August 2026. Organizations face significant penalties for non-compliance, making proactive ethical AI implementation essential for business continuity.
The United States is developing complementary frameworks through executive orders and agency guidance, while other jurisdictions including the UK, Canada, and Singapore are establishing their own AI governance approaches. Organizations operating globally must navigate this complex, evolving regulatory landscape while maintaining consistent ethical standards across jurisdictions.
Strategic Benefits and Business Value
Organizations implementing comprehensive AI ethics programs report measurable benefits beyond regulatory compliance. Trust and reputation enhancement represents perhaps the most significant long-term value, as customers increasingly prefer brands that demonstrate responsible AI use.
Operational benefits include improved AI system reliability, reduced bias-related incidents, and more effective human-AI collaboration. Companies report that ethical AI frameworks lead to better model performance, faster development cycles, and higher customer satisfaction scores.
Risk mitigation advantages include reduced legal exposure, improved regulatory compliance, and protection against reputational damage from AI-related incidents. Organizations with robust ethical AI programs are better positioned to respond to regulatory changes and customer concerns.
Innovation acceleration occurs as ethical frameworks provide clear guidelines for AI development, enabling teams to innovate confidently within established boundaries. This reduces development uncertainty and accelerates time-to-market for new AI-powered customer experience features.
Future Directions and Emerging Trends
The field of AI ethics in customer experience continues to evolve rapidly, with several key trends shaping future development. Enhanced ethical oversight and transparency will require AI systems to be increasingly explainable and understandable, with human-in-the-loop systems gaining prominence in customer-facing applications.
Bias mitigation and fairness will see continued advancement in detection and correction techniques, with regulations targeting discrimination prevention across various sectors. Environmental impact considerations are emerging as organizations assess the carbon footprint of AI technologies and implement sustainability measures.
International alignment and standards development will accelerate as organizations seek consistency across global operations. Industry-specific guidance will emerge for sectors like healthcare, finance, and retail, providing tailored approaches to ethical AI implementation.
Automated ethics monitoring represents an emerging capability where AI systems continuously assess their own ethical performance and alert operators to potential issues. This proactive approach promises to make ethical AI more sustainable and scalable.
Conclusion and Strategic Recommendations
AI ethics in customer experience represents both a critical business imperative and a strategic opportunity for organizations seeking to build sustainable competitive advantages. The convergence of regulatory requirements, customer expectations, and technological capabilities creates a unique moment for organizations to establish leadership in responsible AI deployment.
Strategic recommendations for organizations include:
- Establish comprehensive governance frameworks that integrate ethical considerations into all AI development and deployment processes
- Invest in bias detection and fairness auditing capabilities to ensure equitable customer treatment across all demographics
- Implement transparency and explainability systems that build customer trust through clear communication about AI use
- Develop robust privacy and data governance practices that protect customer information while enabling innovation
- Create meaningful human oversight mechanisms that ensure AI augments rather than replaces human judgment
- Prepare proactively for regulatory compliance, particularly EU AI Act requirements that will influence global standards
The organizations that successfully navigate this transformation will not only achieve regulatory compliance but will establish themselves as trusted leaders in the AI-powered customer experience landscape. By viewing ethical AI as a strategic asset rather than a compliance burden, these organizations will unlock sustainable value creation that benefits customers, employees, and shareholders alike.
The future of customer experience lies in the thoughtful integration of AI capabilities with human values and ethical principles. Organizations that embrace this philosophy today will be best positioned to thrive in tomorrow’s AI-driven business environment, delivering exceptional customer experiences while upholding the highest standards of ethical conduct.